<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>발송이력</title>
<!-- 공통 컴포넌트 관련파일 include -->
<jsp:include page="/webapps/include/TwbInclude.jsp" flush="false"></jsp:include>
<!-- 해당 화면 script파일 include -->
<script src="/html/js/telewebinside/cons/main/TwbSendHistoryTab.js"></script>
<script src="/html/js/include/SystemIDCommon.js"></script>
<!-- 프로젝트에 맞게 공통 스크립트를 확장하여 링크한다. -->
</head>
<body>
<div id="divGridSendHistoryTab"></div>
</body>
</html>
JSP코드에 들어가는 인코딩 문장들에 대해 정리해보자!
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
우선 contentType 이란?
클라이언트에 자원을 보낼 때 HTTP 헤더를 통해 페이지에 대한 세부정보 (소프트웨어 타입, 시간, 프로토콜 등)를 전송함.
*charset=UTF-8 을 통해 웹브라우저가 어떤 캐릭터셋으로 페이지를 받을지 선택한다.*
pageEncoding은 JSP페이지가 어떤 캐릭터셋으로 작성됬는지를 표기한다.
요약
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="MS949"%>
jsp파일은 MS949로 작성되었으며 브라우저는 UTF-8로 받게될 것이다.
다음으로, jsp파일 지시어 다음에 헤드에 들어오는 이 UTF-8은 html의 페이징 캐릭터 셋인다.
<%@ pageEncoding%> 는 jsp인코딩인데
본문의 소스를 굳이 2번씩이나 인코딩해주어야 하나 싶다.
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
* jsp 파일은 서블릿 변환되어 소스파일을 읽으므로 html 캐릭터셋 보다 jsp캐릭터 셋을 더 우선한다.
* 그러므로 지시자에 charset이 선언되어 있으면 html 부문의 meta charset은 무시된다.
소스파일 body에 사용되는 charset 문장은 아래와 같다.
- request.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
- response.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
- response.setContentType("text/html; charset=utf-8");
1) request.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
jsp 혹은 html 에서 작성된 폼 데이터를 전송할 때 UTF-8 방식으로 전송하겠다는 뜻이다.
하지만 GET방식은 URL을 통해 (UTF-8 세팅이 되어있는 톰캣을 거침) 캐릭터 셋 처리를 하기 때문에 톰캣이 세팅된 대로 처리된다.
- html 소스
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<form name="form" action="print2.jsp" method="post">
- 이름 : <input type ="text" name="name"/>
<input type ="submit" value="전송"/>
</form>
</body>
</html>
- jsp 소스
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
String name = request.getParameter("name");
%>
이름은 <%= name %> 이다.
</body>
</html>
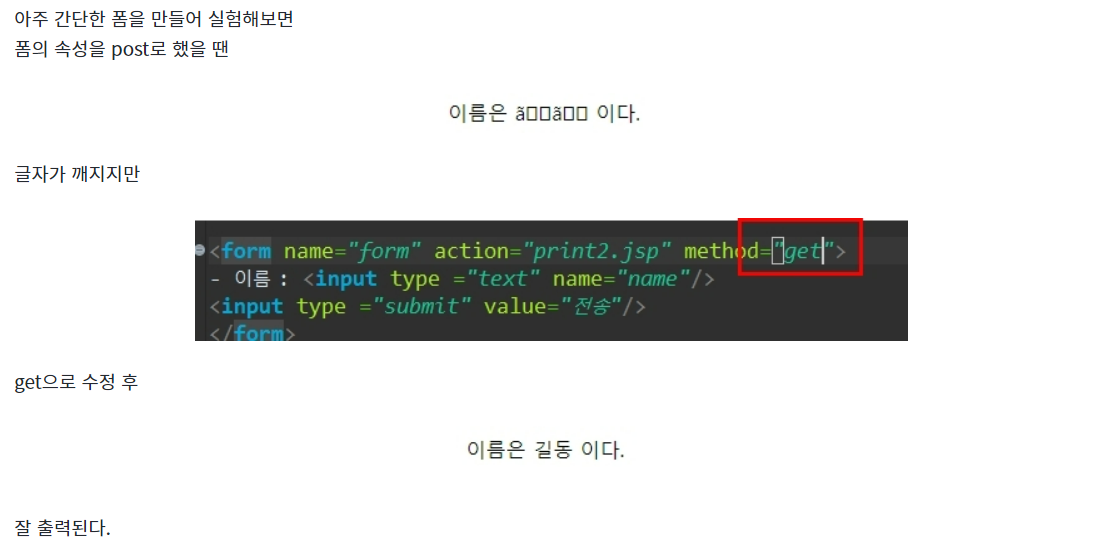
post방식에서도 출력하기 위해서는 폼에서 넘어오는 값을 utf-8로 받아야한다.
▶ request.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
<body>
<%
request.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
String name = request.getParameter("name");
%>
이름은 <%= name %> 이다.
</body>
post방식으로도 잘 출력된다.
한마디로 넘어오는 캐릭터셋을 UTF-8로 요청한다는 것이다.
2) response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8")
브라우저에게 출력형식을 UTF-8로 표현하겠다고 선언하는 문장이다.

3. request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
서블릿으로 넘어오는 파라미터를 utf-8로 출력한다는 문장
두 메소드를 정리하자면
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8"); 는 브라우저에 전송되는 데이터를 인코딩하는것
request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); 는 파라메터(인자)로 전송되는 데이터를 인코딩하는것이다.
요약
pageEncoding="utf-8"%
문서를 어떤 캐릭터 셋으로 작성할지 정하는 것
request.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
이 메소드는 서블릿에서 사용된다. 서버 측으로 데이터를 '요청' 하게 되는데 이 때문에 request 객체를 사용하게 된다.
response.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
이 메소드는 jsp출력에서 사용된다. 즉 서버에서 브라우저로 데이터를 '응답' 할 때 사용하는데 이 때문에 response 객체를 사용한다.
response.setContentType("text/html; charset=utf-8");
contenType이 이 메서드는 브라우저에 표현할 때 어떤 캐릭터 셋을 사용할지 정하는 것
'📌 Front End > └ JSP' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [JSP] <%@ include %>디렉티브 <jsp:include>액션태그 차이점 (0) | 2024.05.21 |
|---|---|
| [JSP] JSP에서 다른 컨텐츠를 포함하는 3가지 방법 <%@ include file="" %> <jsp:include> <c:import> (0) | 2024.05.21 |
| [JSP] jsp파일 include 하기 (0) | 2024.04.30 |


